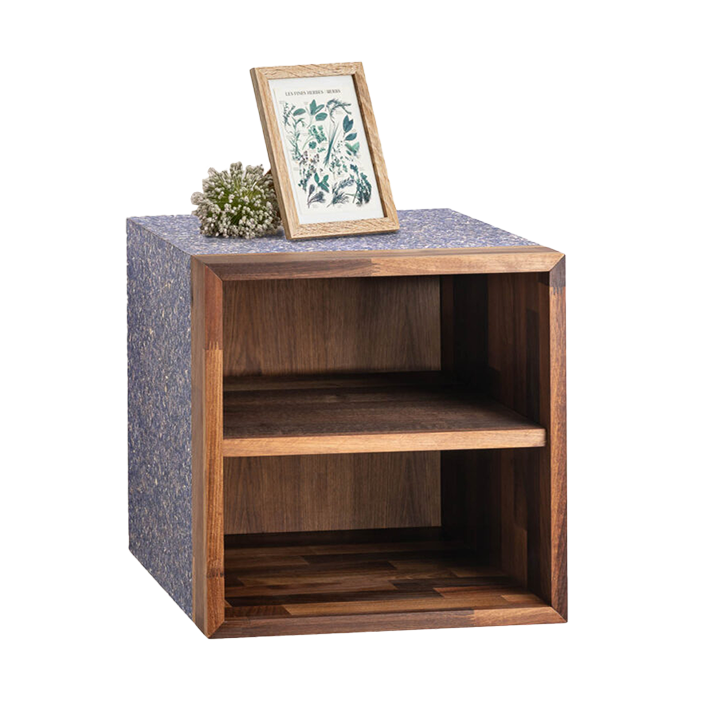
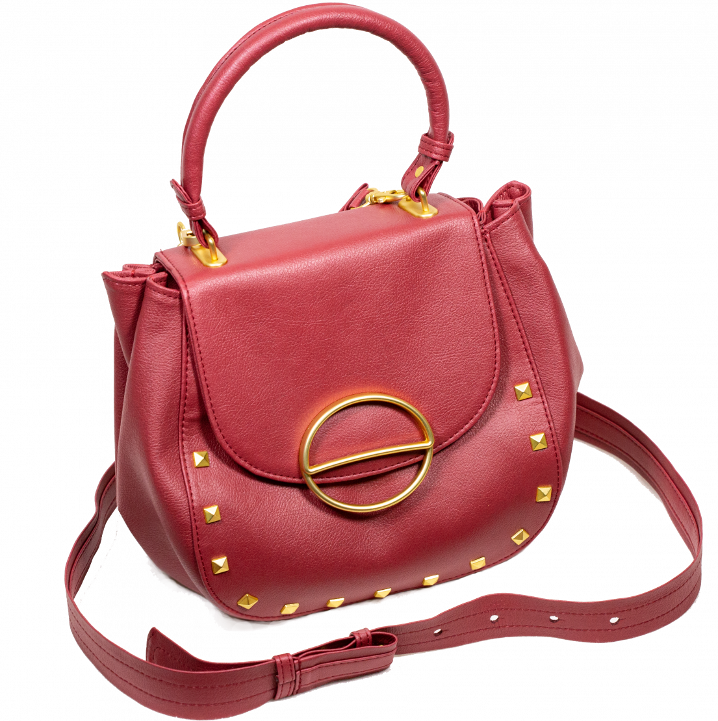
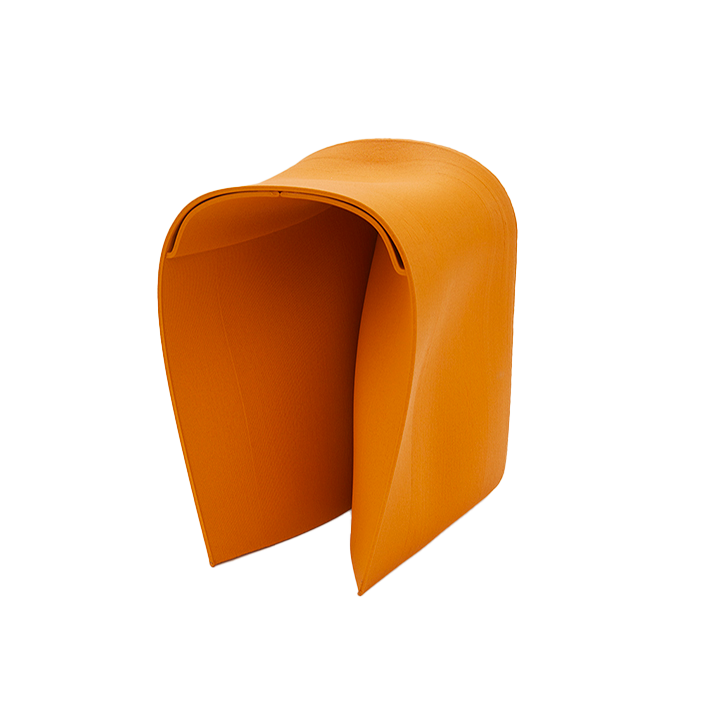
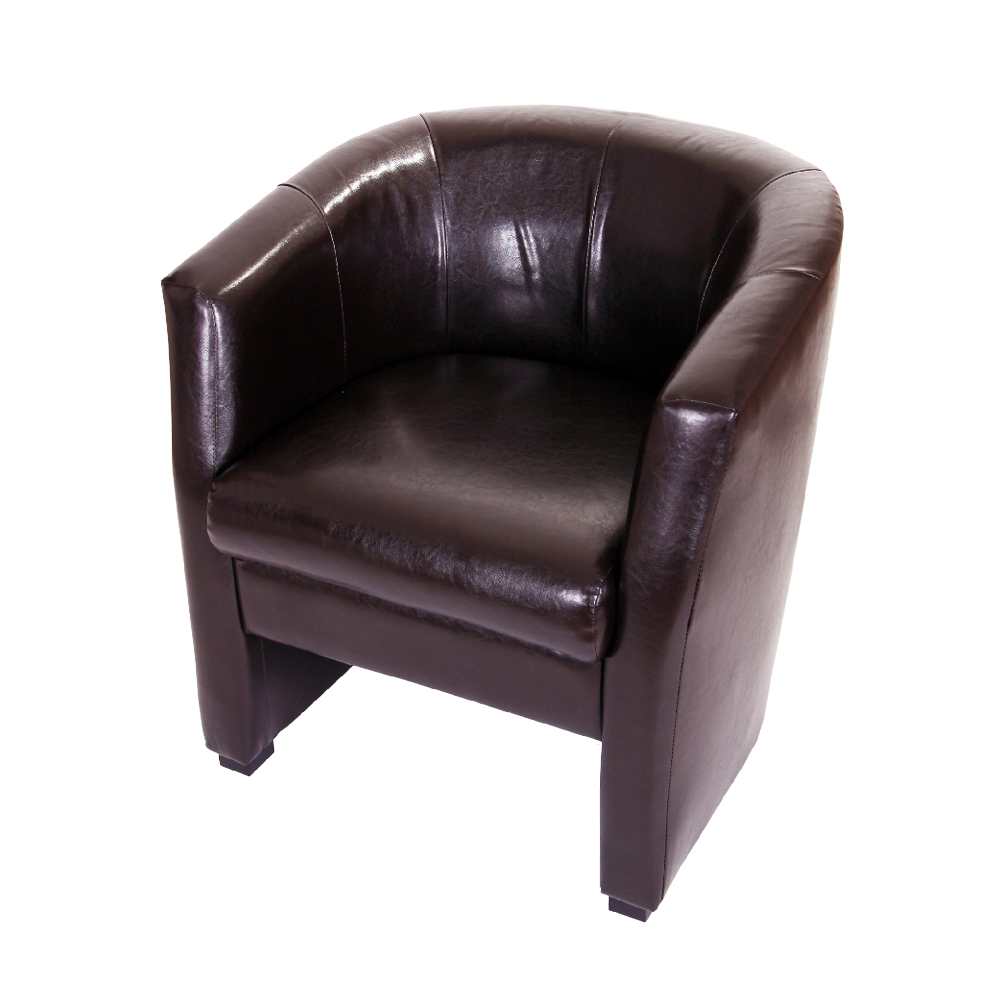
Arm chair
Olive leaves are a waste product from olive harvests and are frequently burned as green waste. They contain valuable ingredients with which biodegradable and skin-compatible premium leather can be produced.
DATA & FACTS
Sector:
Furniture
Renewable resource:
Olive leaves
Participating companies:
wet-green | N-Zyme Biotec
Bioeconomy factor:
Environment-friendly leather tanning
Status:
on the market
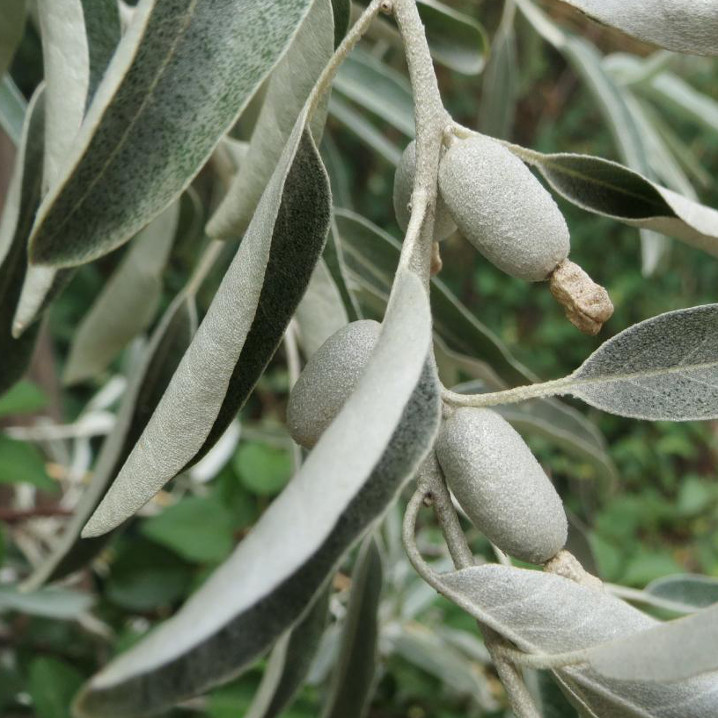


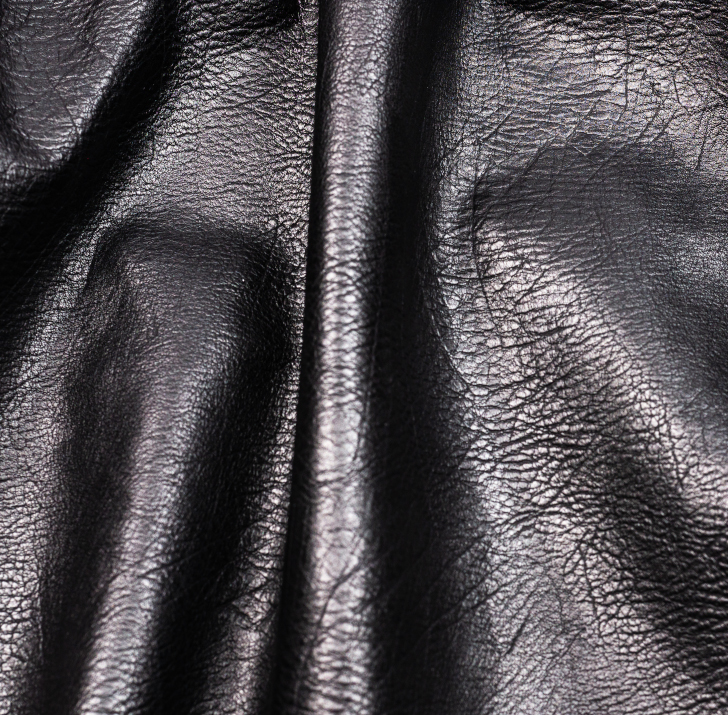
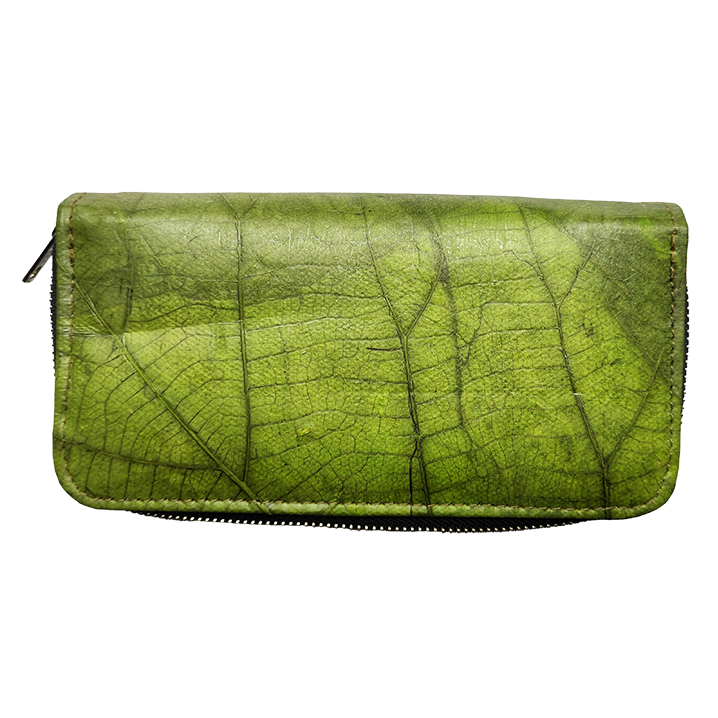
From waste to olive leather
Olive leaves fall by the tonne during the annual harvest of olives in the Mediterranean and until now have been burned as green waste. Two German companies Wet-green GmbH and N-Zyme Biotech GmbH have developed a process that extracts the tannins from the olives leaves in an aqueous solution. This reduces toxic acids and salts in the tanning process. The leather has IMO approval and allows the production of premium leather according to the IVN Natural Leather Standard.
Environmentally friendly tannins
In the industrial production of leather tanning agents, heavy metal salts such as chrome are usually used. Olive leaves are a natural, environmentally friendly alternative. They contain secondary ingredients, which the plants use as a pest defence. This forms the basis for a biodegradable tanning agent. It not only protects the environment, it also makes the leather extremely skin friendly.
Ready for the market
Wet-Green GmbH offers several industrial clients an environmentally friendly process that uses olive leather for their products. Furniture and car manufacturers are already using this procedure.
Weitere Produkte