PAPACKS strengthens partnership with Solenis
The Cologne-based start-up PAPACKS will work even more closely with the US specialty chemicals company Solenis in future to produce sustainable packaging based on hemp on an industrial scale.
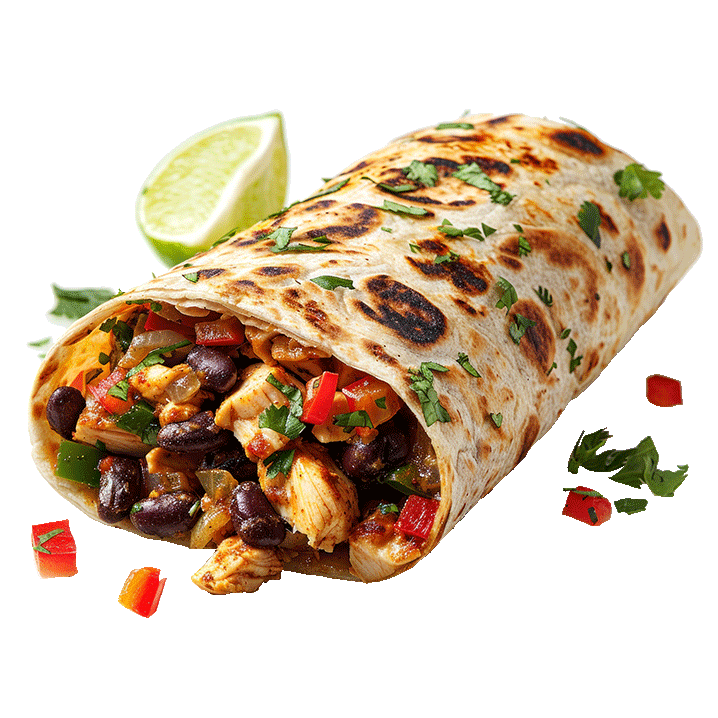
Launch: Koji-based hybrid minced beef
The Berlin-based start-up Nosh.bio is launching a hybrid minced beef product based on koji. It is the first German company to demonstrate the use of koji protein in hybrid minced meat.
Amsilk: Millions for production expansion
The biotech company Amsilk, which specialises in the production of spider silk proteins, has raised tens of millions in fresh capital in a financing round to expand production of the high-tech biomaterial.
BRAIN Biotech: Alliance for new nature-based ingredients
The Zwingenberg-based enzyme specialist BRAIN Biotech will be collaborating with the Dutch company Corbion in the future to develop new sustainable ingredients for food preservation.
Bioeconomy in a Shifting Global Landscape
At the 13th International Bioeconomy Conference in Halle, the spotlight was on the role of the bioeconomy in a world shaped by overlapping crises and evolving geopolitical priorities. In a global economy that is increasingly fragile, companies are under pressure to future-proof their operations - while also confronting the complexities of transitioning away from fossil-based systems.