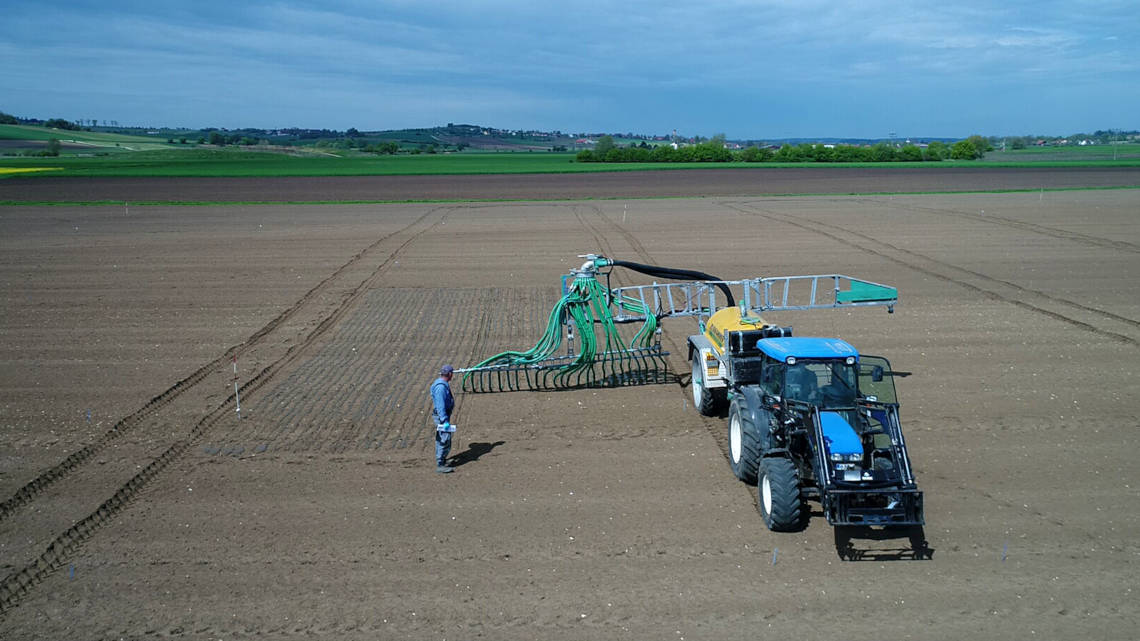
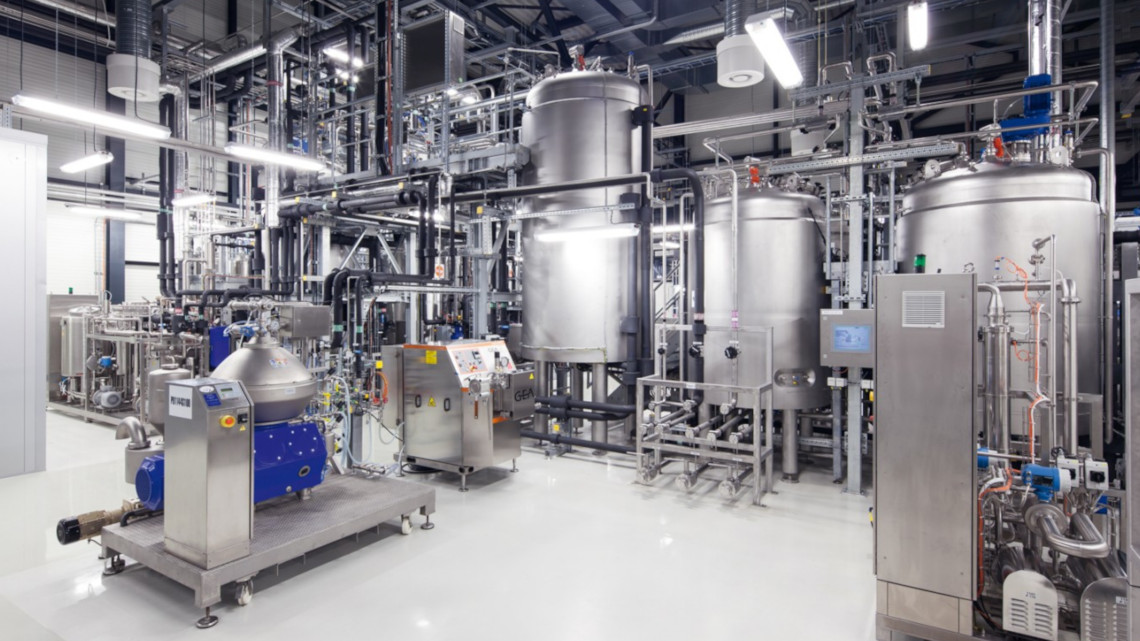
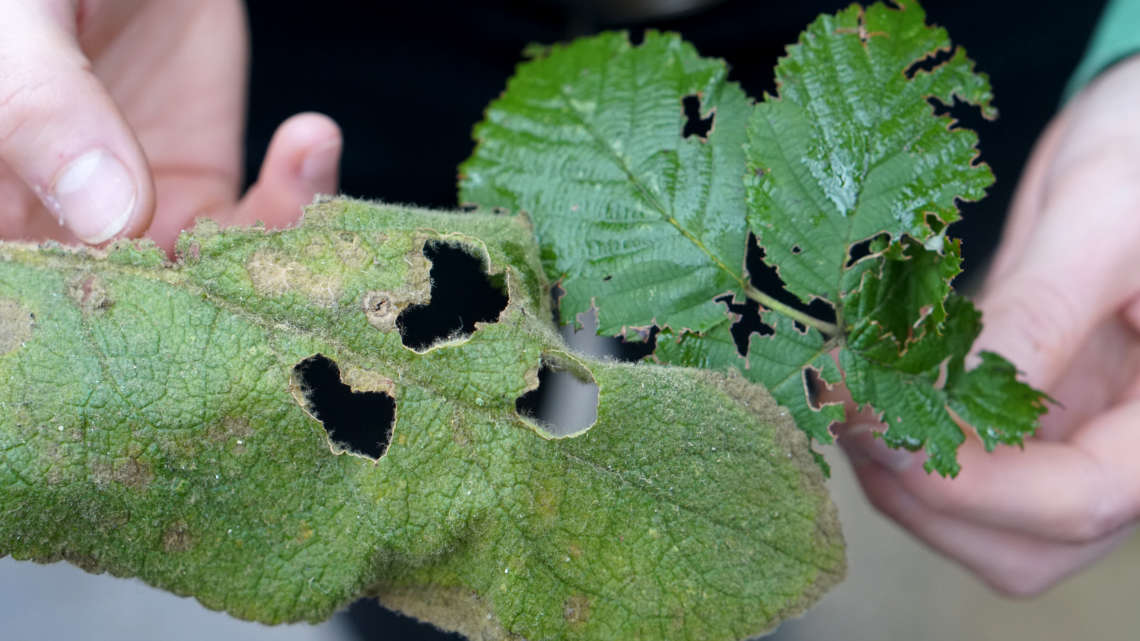
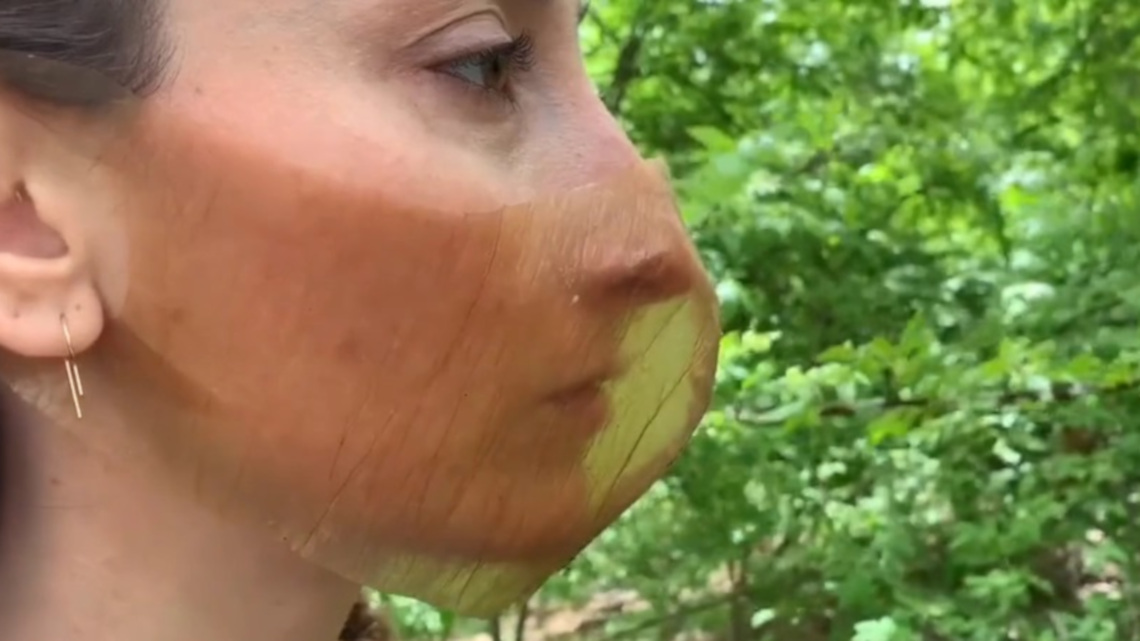
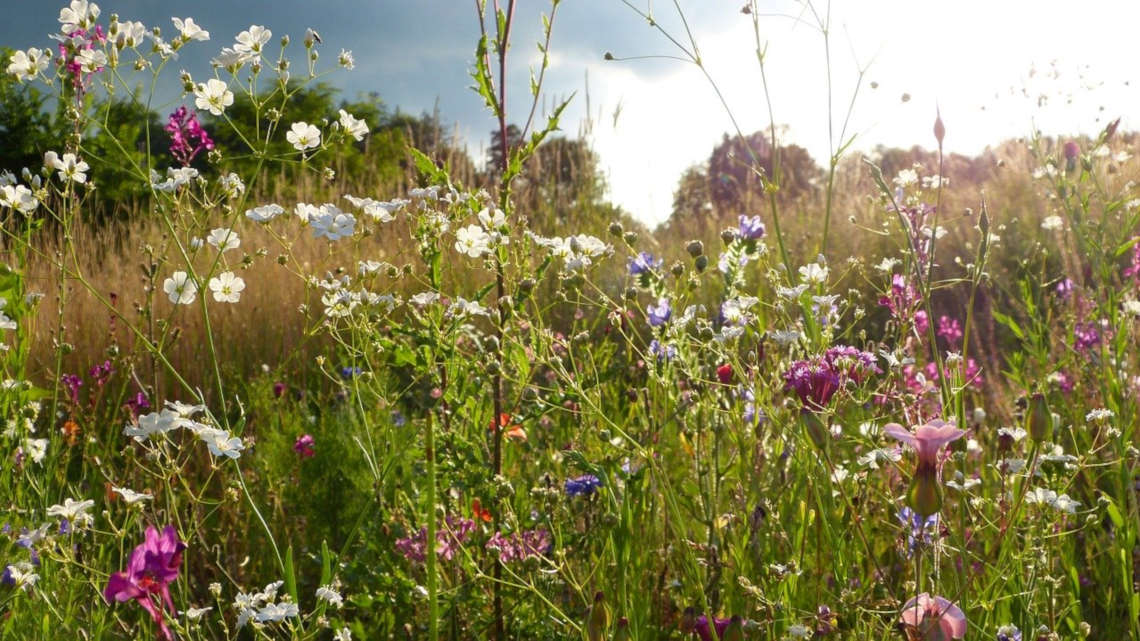
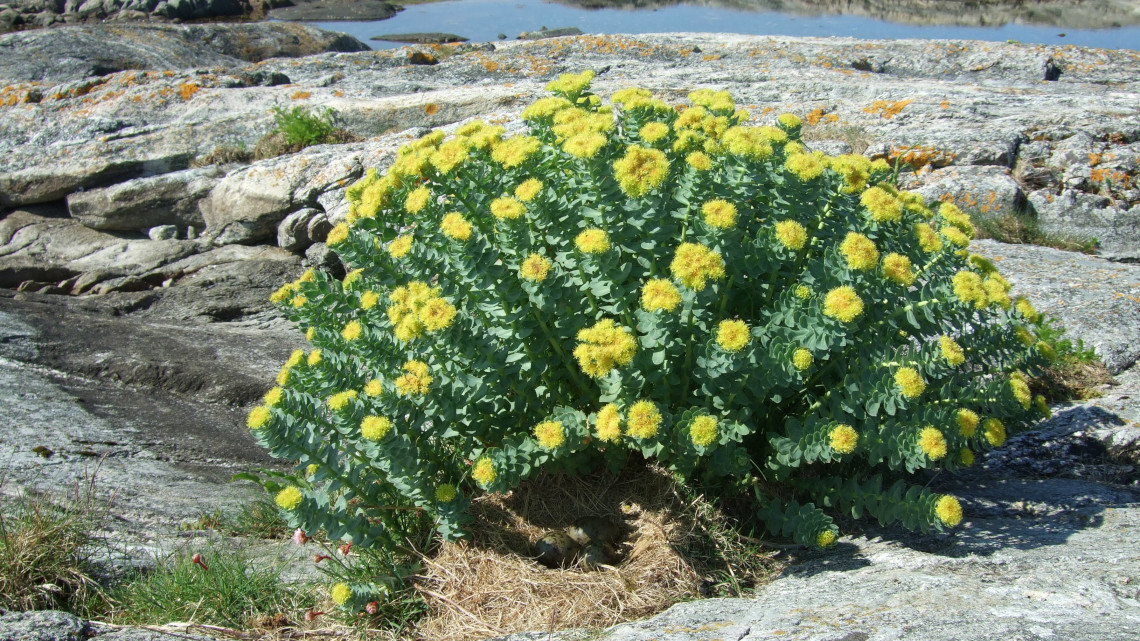
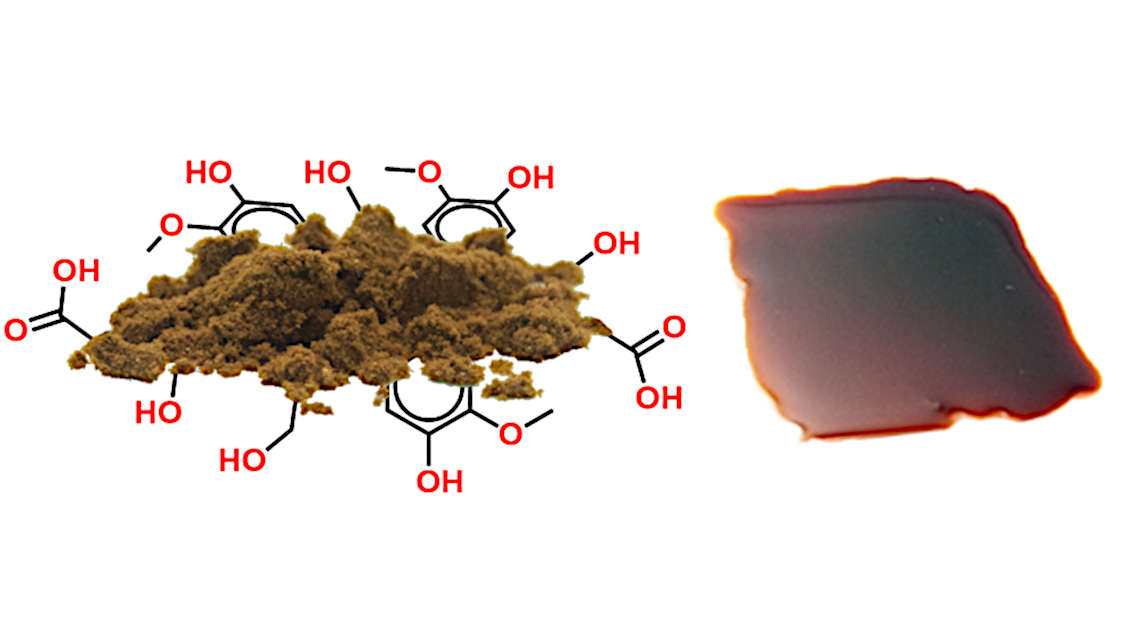
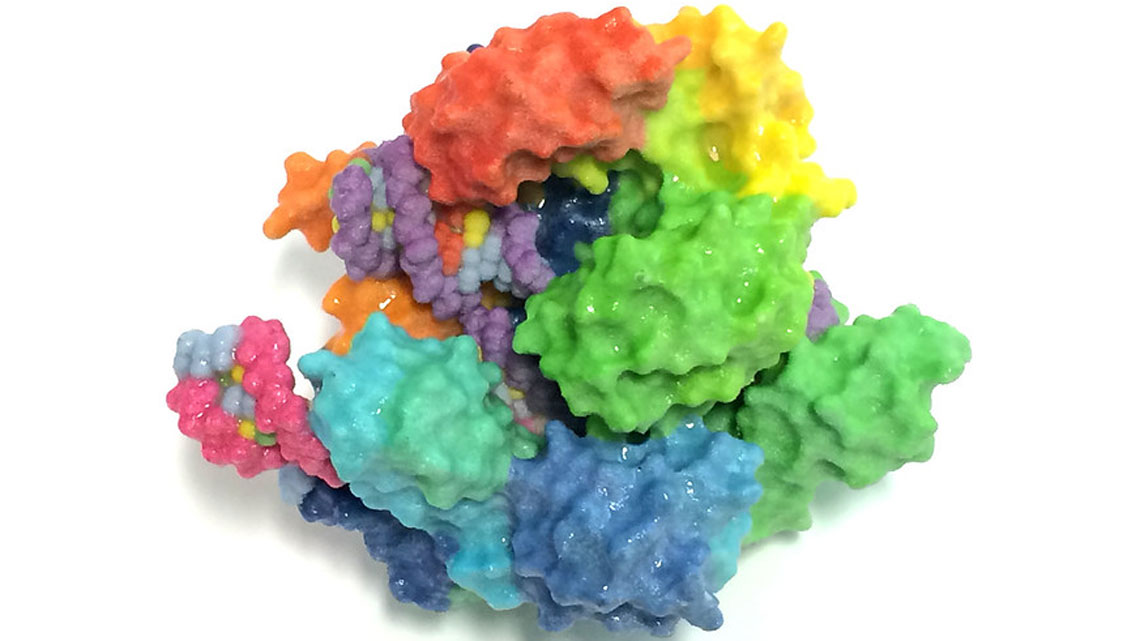
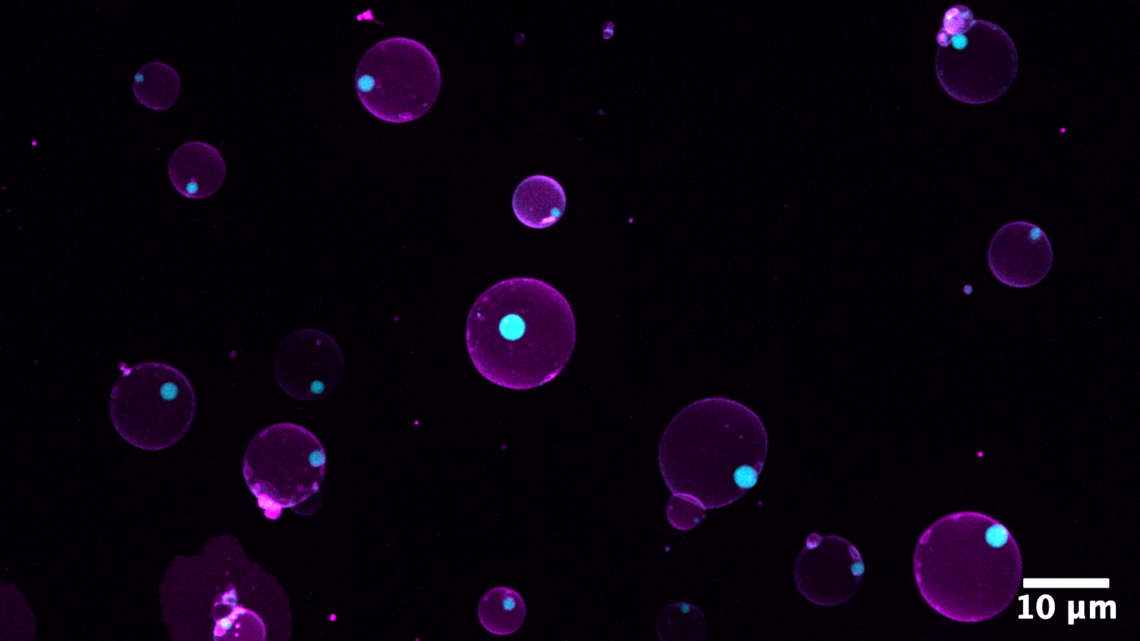
A bioeconomy model farm for Brandenburg
Over the next six years, the state of Brandenburg will provide 25 million euros to support the establishment of a model farm for biobased recycling management at the Leibniz Institute for Agricultural Engineering and Bioeconomy (ATB) in Potsdam.