Textile concrete for sustainable building
Fraunhofer researchers have developed a natural fiber reinforcement for concrete that can be a bio-based alternative to synthetic fibers.

Stability is probably the most important property of concrete. Reinforcements with steel or synthetic fibers serve to give the building material even more stability. But neither steel nor glass or carbon fibers are ecologically sustainable. A team of researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Wood Research (WKI) and Biberach University of Applied Sciences has now investigated whether natural fibers could be an alternative.
Coating largely biobased
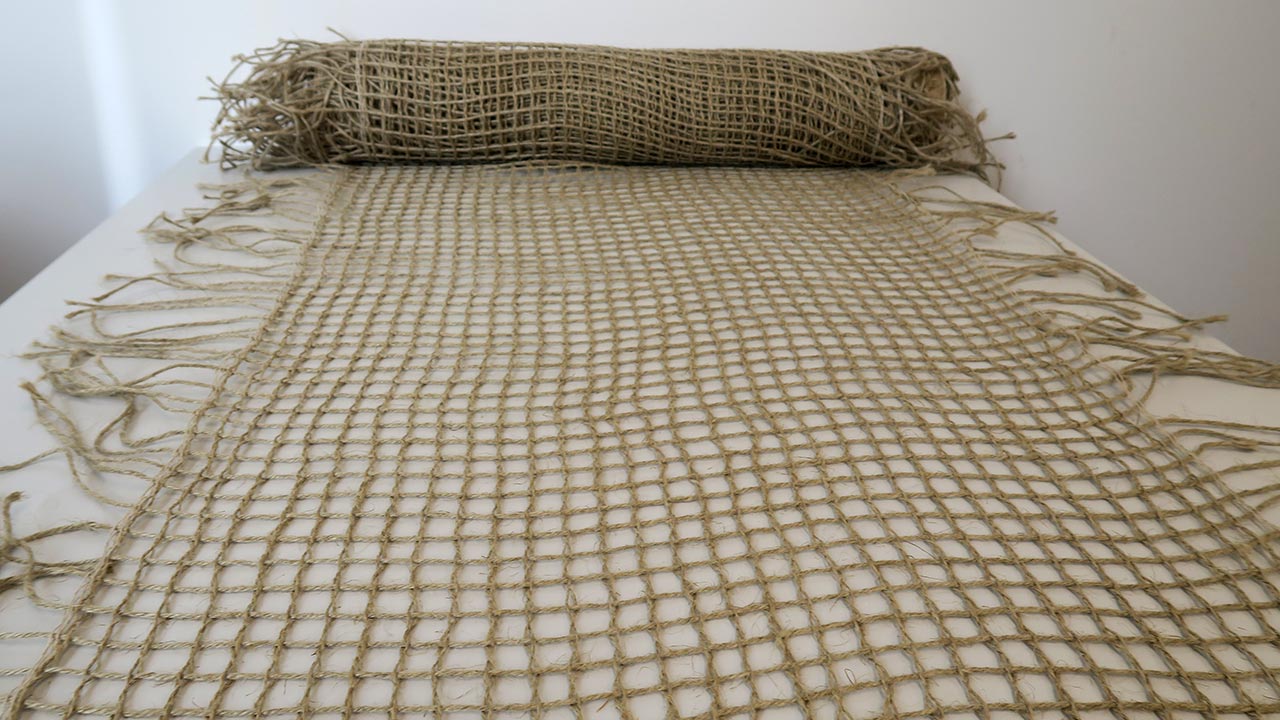
"At the Fraunhofer WKI, we used a weaving machine to produce leno fabrics from flax fiber yarn," reports Jana Winkelmann, project manager at the Fraunhofer WKI. "To make them more sustainable, we tested a treatment of the flax yarns that improves tensile strength, durability and bonding adhesion, which is more ecologically beneficial compared to petroleum-based treatments." In the process, the researchers succeeded in selecting the epoxy resin used for coating so that more than half of it consists of hydrocarbons from plant biomass.
The team then tested the performance of the concrete reinforced with this material - experts refer to composite and tensile load-bearing behavior as well as uniaxial bending behavior. Compared to unreinforced concrete, the test material showed a significantly increased breaking load. The fineness and distribution of the resulting cracks also indicated desirable behavior of the reinforced concrete. The research team therefore concluded that natural fiber-based textile-reinforced concrete components with bio-based impregnation are basically suitable for practical use.
Numerous advantages for practical use
Compared to steel, textile reinforcements have several advantages: They can have the same or higher tensile strength without the risk of corroding. This reduces the thickness of the required concrete cover and allows thinner components with the same load-bearing capacity. If the textile fibers are bio-based, as in the present project, there are further advantages: production requires less energy, less pollution, and it is easier to recycle the fibers later.
"Textile concretes enable lighter and slimmer structures and thus offer architectural scope," summarizes Christina Haxter, a staff member at the Fraunhofer WKI. "We would like to further explore the numerous possible applications of natural fiber-reinforced textile concretes." The current research project expired at the end of 2022. The German Federal Foundation for the Environment had funded it for two years.
bl