BASF: Skin care with bacteria
BASF Care Creations has developed two new cosmetic active ingredients based on probiotics.
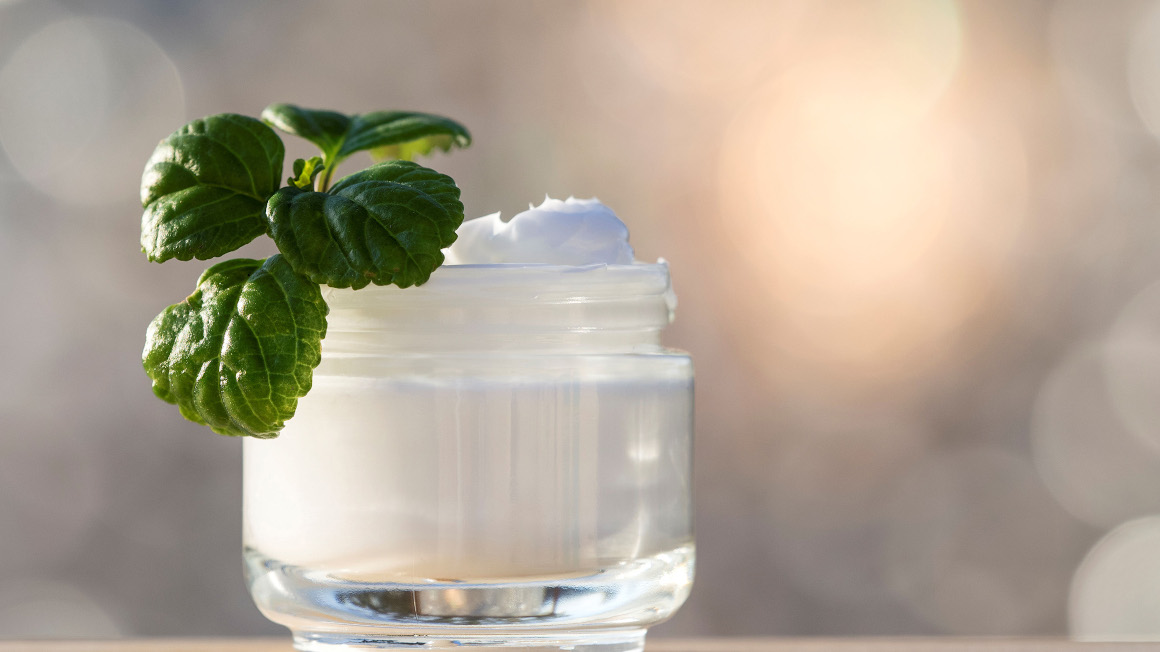

Our skin is home to millions of microorganisms that protect us from pathogens and shape the appearance of our skin. But with age, the skin's microbiome changes. As a result, the skin loses elasticity and wrinkles form. With Probiolift and Postbiolift, BASF's Care Creations division is launching two new cosmetic ingredients that, for the first time, rely on the power of the skin's own bacteria and are designed to help maintain a more youthful and fresh skin.
juvenating cure with skin's own bacteria
According to BASF, both active ingredients contain Lactobacillus crispatus. These are lactic acid bacteria that are part of the natural skin flora. These are abundant on young skin, but increasingly less so with age. "Consumers are increasingly aware of the health-promoting properties of biotic ingredients, whether they are prebiotics, probiotics or postbiotics," says Cécile Kalem, BASF Launch Manager for Cosmetic Ingredients in Europe.
In the food industry, such biotic ingredients have long been firmly established in yogurt, for example. According to Kalem, integrating living skin bacteria into cosmetic formulations and keeping them active has been a problem until now. The chemical company's research and development team has now overcome these hurdles.
Effectiveness confirmed in studies
According to the company, in the active ingredient Probiolift, the living and dormant L. crispatus bacteria become active again when they come into contact with water on the skin, thus increasing skin density and reducing the appearance of forehead wrinkles. The active ingredient Postbiolift, on the other hand, is said to provide more elastic, smoother and more even skin. The efficacy of each of the microbial ingredients was tested in placebo-controlled clinical studies on women, and the results were confirmed in in vitro tests.
bb