Valuable amides from wood waste
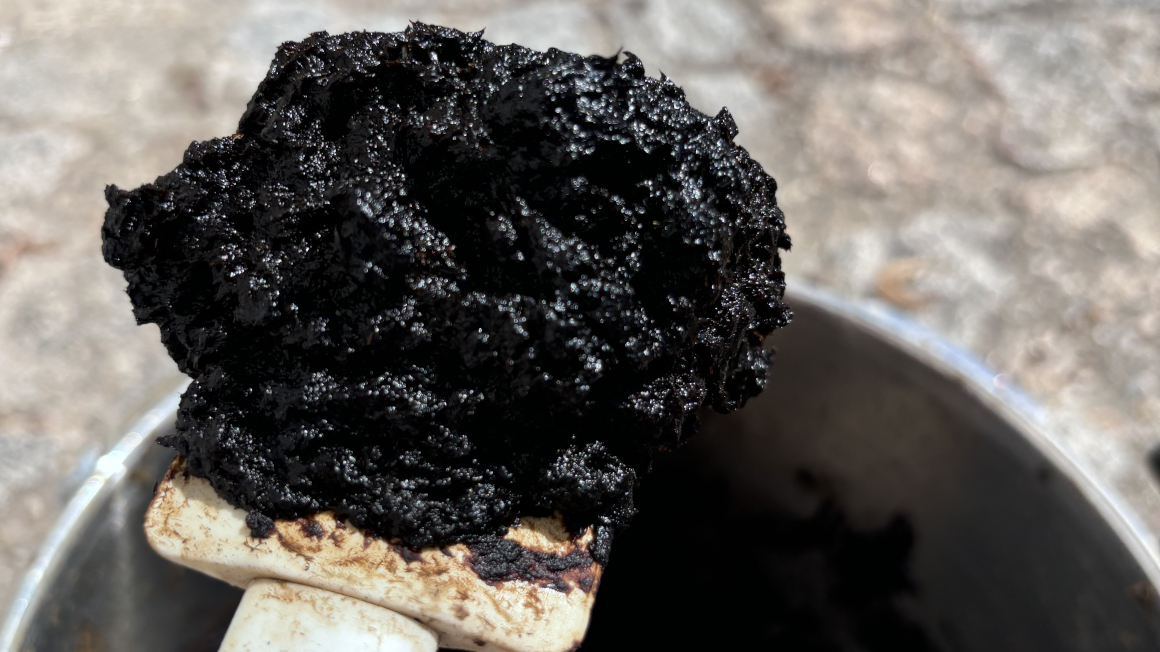
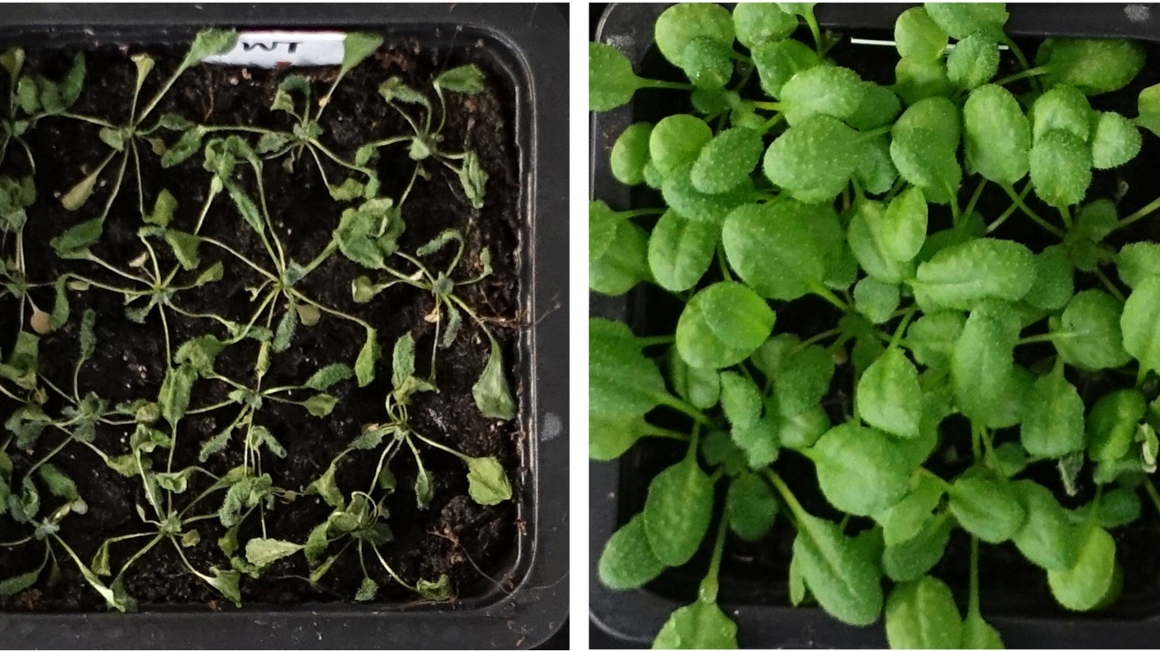
An international research team led by the Leibniz Institute for Catalysis (LIKAT) has developed a new, environmentally friendly process for effectively utilising the plant substance lignin to produce high-quality chemical compounds.